Post by jjohnson on Aug 1, 2020 5:25:26 GMT
This may be a timeline or just a one shot, and has no relation to my other timeline. You may have to click the images to get a larger size.
Alternate History:
The first and second world wars happen essentially the same, aside from the addition of the Confederate States, which cooperate with the United States in all theaters. Fighting wars with the United States does much to help the two nations improve their views of one another, despite having occasional differences of opinions.
After the first world war, the Confederates were slightly more true to the Wilsonian 'ethnic self-determination' idea and pressed the allies to make some changes to their original borders - Austria would keep the German-occupied areas (South Tyrol, Preßburg, Ödenburg, South Bohemia/Moravia, Sudetenland, German Bohemia, Teschen Silesia) but be forbidden to merge with Germany. Germany would lose Posen, Memelland, Alsace-Lorraine, and a little bit of Silesia. Its northern border would shift, but Tonder would remain in Germany, as would Logumkloster and a few other communities. Greece was able to retain Constantinople due to the Confederate presence, and Hungary was able to annex the portion of Slovakia with a Hungarian majority. Alsace-Lorraine would form a neutral nation between Germany and France so as to prevent war between the two nations.

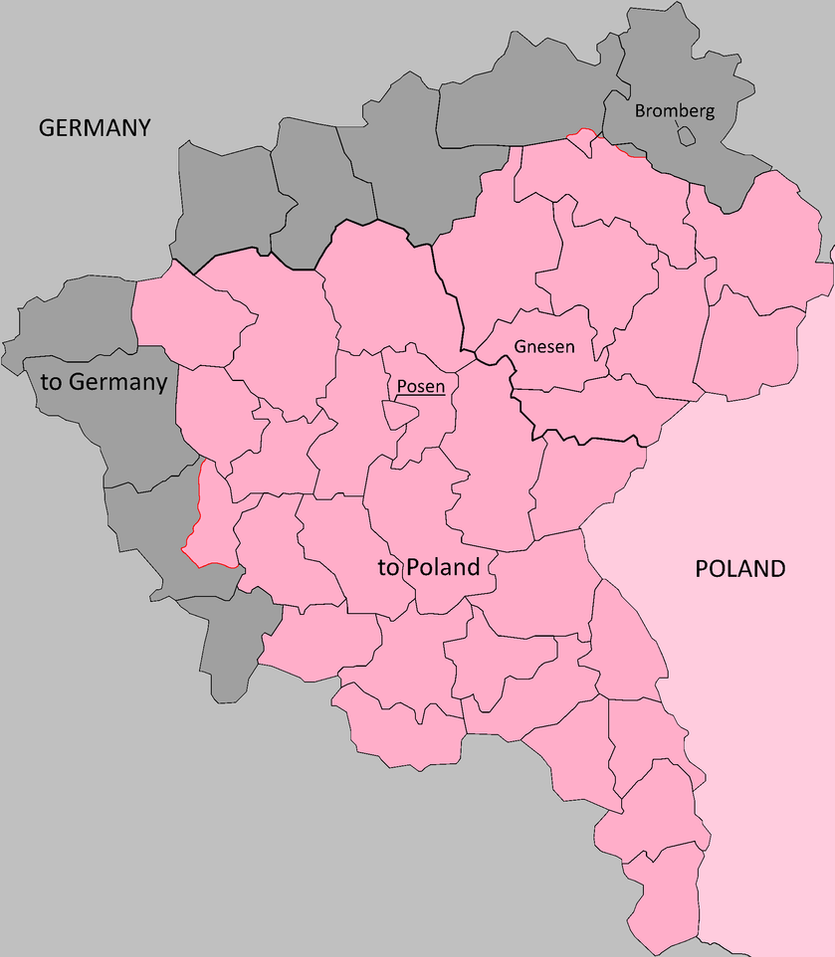
Czechoslovakia as of 1919; Posen ceded to Poland, aside from the contiguous counties, which would join Brandenberg and West Prussia.
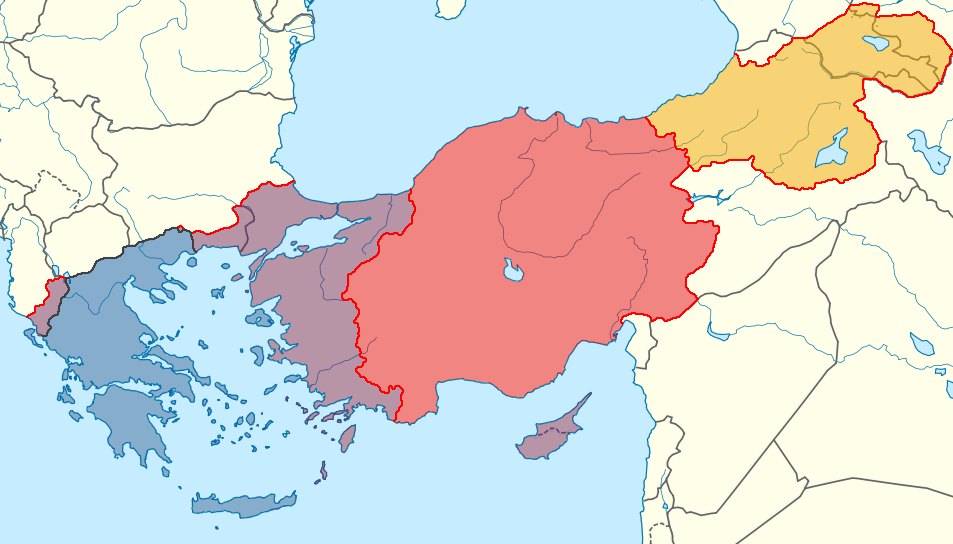
Post-WW1 Asia Minor. Note Greece, Turkey, and Armenia. Due to Turkey's noted genocides of Armenians and Greeks, Turkey was forced to acknowledge and pay reparations to the two nations.
After the end of the second world war, US President Robert Taft and CS President William Tuck of Virginia came at loggerheads with the state of post-war Europe. The Confederates were more afraid of the Soviets than Taft and all his advisers, and did not want to allow them to push the line of Soviet occupation all the way past Berlin. Taft argued for the Curzon Line and pushing the Germans out of East Prussia, Danzig, Silesia, the Neumark of Brandenburg, and Pomerania. Confederates remembered their experience with Missouri and West Virginia in their own independence war with the US, and had a large number of Texas Germans so they had more in common with them than the Russians, despite the war. Taft was eager to get a solution, so Tuck gave Taft and Stalin a compromise - restore West Prussia, and all of that can be a Soviet Occupation zone and have the Curzon line be halfway between the proposed line and the existing eastern border.

So after the war, Poland didn't gain as much land, other than keeping Posen. Lithuania gained a little of upper Poland, and both Ukraine and Belarus gained from Poland. Moldova gained Alba from Romania to gain seaport access. The Soviet Occupation Zone was set up as the German Social Democratic Republic (DSDR), while the western portion would be set up as the Confederated Republic of Germany (KRD). The Confederates, Americans, and British "helped" the Germans write their West German Constitution, the Verfassung der Verbundeten Republik Deutschlands.
Excerpt, Article 1: Fundamental Rights of the German People
Section 1: Individual Rights
(1) The citizens of Germany have the right to life and to physical integrity, which shall not be infringed from natural life to natural death. The right to life may only be abridged upon conviction of a capital crime. The right to physical integrity shall include the right not to be medically experimented upon, the right not to be forced to take any medication as a condition of education, employment, or exercising any right.
(2) The citizens of Germany have the right to human dignity, which shall be respected and protected by the state authority.
(3) The people of Germany acknowledge that all people have inviolable and inalienable human rights, which include the right to life, liberty, property, worship, assembly, petition, speech, and the press.
(4) The citizens shall have the right to speak freely by any means or technology, which shall have the right to disagree with the government, its policies, and its officials and to expose corruption and crimes, and the right to speak even if it offends another person. There shall be no censorship other than nudity, violence, or to protect the innocence of children.
(5) The citizens shall have the freedom of religion, which shall include the right to worship without government interference as to the content or manner or other means, and shall include worship in any place. The government shall not establish a religion or mandate the religion or worship of others.
(6) The citizens shall have the right to assemble peaceably and to petition the government for a redress of grievances
(7) The freedom of the press shall not be infringed; the government shall not fund the press, nor provide or require propaganda for the press to disseminate, nor compel the press to release or not release a story for grounds other than national security.
(8) The people shall have the right to travel freely throughout the territory of Germany, and to resettle between cities and states. This may be restricted to prevent crime, avert imminent danger to the constitutional order, or to combat an epidemic or natural disaster.
(9) All citizens shall be equal before the law without regard to race, gender, parentage, language, religion, political opinions, homeland, or origin, and shall not be favored or disfavored on account of such reasons.
(10) All citizens have the right to bear arms and the right to self defense and the defense of home, family, and property, and this right shall not be infringed.
(11) Education shall be the responsibility of the state governments, without interference from the federal government; the citizens shall have the right to choose their means of education, whether publicly funded school, privately funded school, religious school, or home school, and parents shall have the right to choose the education of their children.
(12) Arts and sciences, research, and teaching shall be free from government funding, regulation, but the freedom of teaching, and science and research shall not release any person from allegiance to the constitution and respect for the rights of other persons.
(13) Marriage between one man and one woman and the family that results shall be protected by the state. Parents shall be responsible for the care and upbringing of their children with the state ensuring the fulfillment of this duty. Children may be separated from their families against the will of their parents or guardians only pursuant to law, which shall not include disagreement with the political or religious opinions of the parents and guardians that are in accord with allegiance to this constitution.
(14) The people have the right to form corporations and other associations, so long as those associations and corporations do not aim to contravene criminal laws, or are directed against the constitutional order or the concept of international understanding.
(15) The people have the right to the privacy and security of their correspondence and communications made by any means.
(16) All persons have the right to work and to choose their occupation or profession, their place of work, and their place of training, and shall not be infringed on the basis of religion or political opinion.
(17) All persons have the right not to be enslaved. Forced labor shall not exist within Germany other than as punishment for a crime for which he shall have been duly convicted in accordance with law.
(18) The people shall be free from all searches and seizures except by a specific warrant in accordance with law, which shall name the time, manner, place, and things sought or searched.
(19) The right to property shall include the right to acquire, use, and dispense with that property. Property shall not be seized without just and speedy compensation.
(20) Men and women may be required to serve in the armed forces, federal border police, or in a civil defense organization upon reaching the age of eighteen.
(21) No German may be deprived of his citizenship except by applicable law, unless it shall result in the person becoming stateless as a result.
(22) No German shall be extradited to a foreign country except by treaty between Germany and the foreign country explicitly stating the conditions thereof.
(23) Persons of German ancestry shall have the right of return to Germany in accordance to law.
(24) Persons persecuted on political or religious grounds shall have the right of asylum in accordance with law.
(25) The freedom of speech, press, education, teaching, assembly, correspondence, association, privacy of correspondence, property, or asylum shall not include the right to overthrow the constitution or the republican form of government, and such person or persons shall forfeit their basic rights in accordance to law.
(26) The preceding basic rights shall bind the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary as directly applicable law.
The German President would have a six year term, with one reelection, as head of state. The Chancellor would be head of government. The Bundestag would consist of the upper house (Landtag) and lower house (Volkstag). From the end of WW2 until 1991, Germany would remain divided between east and west. Germans living in all other countries of Europe were expelled to Germany. The Gottschee Germans were deported to Austria, as were all other German-speakers, including Transylvanian Saxons, from the former Austria-Hungary, to Austria. The Volga Germans were resettled in the now East Germany, adding around 950,000 new persons, along with another roughly 2.8 million from Soviet Europe to be moved into East Germany.
The Germany that came out of the war had 14 states (Bremen, Hamburg, Lübeck, West Berlin, Bavaria, Baden, Württemberg, Alsace-Lorraine, Rhineland, Palatinate, Hessen, Lower Saxony, Oldenburg, Schleswig-Holstein), while the Soviet sector, which became East Germany, had 11 states (Mecklenburg, Pomerania, Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Saxony, Upper Silesia, Lower Silesia, West Prussia, East Prussia, Berlin) which would be converted into 22 Bezirke (districts) so as to more effectively manage them and remove historic ties to the former states. The Berliner Schloss is left in ruin during the entire reign of East Germany. East Germany paid reparations to Poland and the USSR in the form of agricultural output and industrial output. West Germany paid monetary compensation to the west, but when the US put bases in West Germany, the cost of those bases was deducted from the reparations to the US.
West Germany becomes a capitalist beacon, but not in the model of the United States, but rather a European model. Markets are little regulated beyond customer safety, measurements and such. Health care is privatized with insurance for emergencies, while elderly have drug, doctor, and routine procedure insurance plans similar to US medicare, but with more private innovation to reduce the federal outlays. Social insurance does exist, but is funded by private contributions like the US 401k, along with taxes up to 5% to ensure everyone gets something, and people can contribute up to 30% of their income to their social insurance (for retirement, unemployment, and disability). Federal income tax cannot exceed 15%, and state income tax cannot exceed 10%. The West German Mark is introduced in 1948 and West Germany undergoes its Wirtschaftwunder much as in OTL. The West German government, due to Confederate insistence, is much leaner than it had been under the German Empire, Weimar Republic, or Nazi Germany, and is about midway between that of the CS and US, with its regulation and taxation closer to that of the CSA.
East Germany is more capable than OTL since it has Silesian industry, though it was hindered due to Soviet attempts to dismantle and transport back to the USSR initially. Once that stopped, East Germany became the industrial giant of the Warsaw Pact, though its one-party rule, over-regulation, monetary controls, and oppressive spy grid made economic innovation grind to a halt. By the 1980s there were serious signs of trouble, and by 1989, even the excess industrial capacity of Silesia was grinding to a halt as communism faltered.
Once communism fell and the two Germanies reunited, however, West Germany created a plan to bring the east up to western standards, whereby eastern companies would be invested in by the west, given loans with favorable terms, and use those loans to purchase modern equipment to replace old, worn out, and outdated equipment. Eastern German companies struggled through the 1990s but with West German aid, they were able to make the turnaround after a few years.

Continental United States (1948)
After its war with the Confederates, the United States signed a treaty which recognized their new border at the 37th parallel west of the Mississippi, aside from the 'Nevada Notch,' and the Confederates would recognize West Virginia and Missouri as US territory, and both would resume peaceful relations afterwards. The US went on to acquire the Solomon Islands, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, the Marshall Islands, and St Barts. During the war, the US occupied Greenland, a Danish territory, and would buy it in 1948 once the Soviets made their moves in Germany that same year to create a satellite nation. This United States is much like our United States, with a federal reserve, income tax, and much the same history, save the loss of the southern portion in 1865. Its presidents were largely the same, and included Woodrow Wilson, whose parents chose to remain in the US by moving to Maryland. This United States also imported Nazi scientists via Operation Paperclip, but shared the scientific knowledge with the Confederate States, which participated in the operation but would not accept any Nazis into their country, as the distaste for the ideology wouldn't allow it.

Continental Confederate States
The Confederate States were a devastated nation that barely survived their war of secession. Sherman and Grant destroyed as much private property as they could, and kept up the heat as much as they could to use the manpower advantage. But the Confederates turned the tide at Atlanta with Johnston against Sherman, and the Cleburne Memorial's being put into effect in 1864 solved the manpower problems. Aside from its new 37th parallel border, the Confederates stumbled into a near-war with Mexico that they negotiated out of with France, and purchased Alaska from the Russians in exchange for not prosecuting John Turchin and promising a good deal on cotton exports. This version of the CSA purchased the Dominican Republic for its resources (land for tobacco, sugar, cocoa, coffee), and found itself stumbling into war with Spain over Cuba due to its officers helping Cuban rebels; this resulted in the acquisition, after an 11-month war, of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Mariana Islands. Spain sold the Philippines to the US to help pay for the war costs afterwards. Rebuilding was in the Confederate interest, as the British and French interest and helped the economy rebound quickly. This CSA progressed forward to such a point that by 1896, blacks had the constitutional right to vote, though it would be until 1921 when effective legislation would pass that ensured it. Hawaii was annexed in 1874 after attempted coups by the US and UK, seeking protection with the CS. The CS joined WW1 with the destruction of the Lusitania, the US following a few months afterwards. The CS joined WW2 when its fleet at Pearl Harbor was attacked. This CSA has a much lower government footprint than the United States, such that, even after the second world war, Confederates had little to no interactions with their national government, the states being more of the focus of their loyalties and interactions. There is no national bank, no national income tax, and only some states have an income tax. Education is a state issue, funded by tuition, not property tax. Income is on par with the United States, about $1350, but without a national income tax, Confederates keep more of their money. Corporations, however, do have an income tax, but it's a flat tax for the duration of the war. War brides were a thing for the Confederates, much more than the US, with French, British, Dutch, Belgian, German, Italian, Australian, New Zealander, and Japanese brides making up over 550,000 new immigrants into the CS, not including children.
-----
1991
Communism collapsed across eastern Europe for a variety of reasons, and in Berlin, the wall came down to the delight of the German people long separated by concrete, barbed wire, and watch towers. Reunification day was October 3, and the eastern territories were reconstituted legally into their original, pre-1914 borders, undoing quite a few border changes made by the former East Germany. Underground churches, funded by a number of Confederates secretly, kept religion alive in the east, and hope in a brighter future. After the fall of the wall, eastern Germans did flood west, but investment and people flowed east as well. Per the treaty at the end of WW2, the US, CS, UK, and Russia must agree to German reunification.
2000
------
European unification proceeds with the Euro. Economic Union grows as the Schengen border agreement takes place, and Straßburg becomes the seat of the European Parliament, being based in the neutral country of Alsace-Lorraine, a bilingual nation and a symbol for reconciliation and cooperation between France and Germany after the war. The Euro zone begins operation with France, Germany, Spain, Portugal, Austria, Greece, Denmark, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium, Czechia, Slovenia, and Alsace-Lorraine.
2021
-------
After thirty years of unification, the east does continue to have a lower income and level of religion than the west, but both are improving and are continuing to increase. Former buildings, like the Dresden Frauenkirche, the Memorial Church on the side of the Berlin Cathedral, Schloß Charlottenberg, Berliner Schloß, Reich Chancellery (now the Konföderierungskanzlerei), and more are rebuilt to their former appearance and function. The Berliner Schloß is the President of Germany's residence in the city (as of 2009), as Schloß Bellevue did not have room for the President and the government functions for which he is responsible.
Alternate History:
The first and second world wars happen essentially the same, aside from the addition of the Confederate States, which cooperate with the United States in all theaters. Fighting wars with the United States does much to help the two nations improve their views of one another, despite having occasional differences of opinions.
After the first world war, the Confederates were slightly more true to the Wilsonian 'ethnic self-determination' idea and pressed the allies to make some changes to their original borders - Austria would keep the German-occupied areas (South Tyrol, Preßburg, Ödenburg, South Bohemia/Moravia, Sudetenland, German Bohemia, Teschen Silesia) but be forbidden to merge with Germany. Germany would lose Posen, Memelland, Alsace-Lorraine, and a little bit of Silesia. Its northern border would shift, but Tonder would remain in Germany, as would Logumkloster and a few other communities. Greece was able to retain Constantinople due to the Confederate presence, and Hungary was able to annex the portion of Slovakia with a Hungarian majority. Alsace-Lorraine would form a neutral nation between Germany and France so as to prevent war between the two nations.


Czechoslovakia as of 1919; Posen ceded to Poland, aside from the contiguous counties, which would join Brandenberg and West Prussia.

Post-WW1 Asia Minor. Note Greece, Turkey, and Armenia. Due to Turkey's noted genocides of Armenians and Greeks, Turkey was forced to acknowledge and pay reparations to the two nations.
After the end of the second world war, US President Robert Taft and CS President William Tuck of Virginia came at loggerheads with the state of post-war Europe. The Confederates were more afraid of the Soviets than Taft and all his advisers, and did not want to allow them to push the line of Soviet occupation all the way past Berlin. Taft argued for the Curzon Line and pushing the Germans out of East Prussia, Danzig, Silesia, the Neumark of Brandenburg, and Pomerania. Confederates remembered their experience with Missouri and West Virginia in their own independence war with the US, and had a large number of Texas Germans so they had more in common with them than the Russians, despite the war. Taft was eager to get a solution, so Tuck gave Taft and Stalin a compromise - restore West Prussia, and all of that can be a Soviet Occupation zone and have the Curzon line be halfway between the proposed line and the existing eastern border.

So after the war, Poland didn't gain as much land, other than keeping Posen. Lithuania gained a little of upper Poland, and both Ukraine and Belarus gained from Poland. Moldova gained Alba from Romania to gain seaport access. The Soviet Occupation Zone was set up as the German Social Democratic Republic (DSDR), while the western portion would be set up as the Confederated Republic of Germany (KRD). The Confederates, Americans, and British "helped" the Germans write their West German Constitution, the Verfassung der Verbundeten Republik Deutschlands.
Excerpt, Article 1: Fundamental Rights of the German People
Section 1: Individual Rights
(1) The citizens of Germany have the right to life and to physical integrity, which shall not be infringed from natural life to natural death. The right to life may only be abridged upon conviction of a capital crime. The right to physical integrity shall include the right not to be medically experimented upon, the right not to be forced to take any medication as a condition of education, employment, or exercising any right.
(2) The citizens of Germany have the right to human dignity, which shall be respected and protected by the state authority.
(3) The people of Germany acknowledge that all people have inviolable and inalienable human rights, which include the right to life, liberty, property, worship, assembly, petition, speech, and the press.
(4) The citizens shall have the right to speak freely by any means or technology, which shall have the right to disagree with the government, its policies, and its officials and to expose corruption and crimes, and the right to speak even if it offends another person. There shall be no censorship other than nudity, violence, or to protect the innocence of children.
(5) The citizens shall have the freedom of religion, which shall include the right to worship without government interference as to the content or manner or other means, and shall include worship in any place. The government shall not establish a religion or mandate the religion or worship of others.
(6) The citizens shall have the right to assemble peaceably and to petition the government for a redress of grievances
(7) The freedom of the press shall not be infringed; the government shall not fund the press, nor provide or require propaganda for the press to disseminate, nor compel the press to release or not release a story for grounds other than national security.
(8) The people shall have the right to travel freely throughout the territory of Germany, and to resettle between cities and states. This may be restricted to prevent crime, avert imminent danger to the constitutional order, or to combat an epidemic or natural disaster.
(9) All citizens shall be equal before the law without regard to race, gender, parentage, language, religion, political opinions, homeland, or origin, and shall not be favored or disfavored on account of such reasons.
(10) All citizens have the right to bear arms and the right to self defense and the defense of home, family, and property, and this right shall not be infringed.
(11) Education shall be the responsibility of the state governments, without interference from the federal government; the citizens shall have the right to choose their means of education, whether publicly funded school, privately funded school, religious school, or home school, and parents shall have the right to choose the education of their children.
(12) Arts and sciences, research, and teaching shall be free from government funding, regulation, but the freedom of teaching, and science and research shall not release any person from allegiance to the constitution and respect for the rights of other persons.
(13) Marriage between one man and one woman and the family that results shall be protected by the state. Parents shall be responsible for the care and upbringing of their children with the state ensuring the fulfillment of this duty. Children may be separated from their families against the will of their parents or guardians only pursuant to law, which shall not include disagreement with the political or religious opinions of the parents and guardians that are in accord with allegiance to this constitution.
(14) The people have the right to form corporations and other associations, so long as those associations and corporations do not aim to contravene criminal laws, or are directed against the constitutional order or the concept of international understanding.
(15) The people have the right to the privacy and security of their correspondence and communications made by any means.
(16) All persons have the right to work and to choose their occupation or profession, their place of work, and their place of training, and shall not be infringed on the basis of religion or political opinion.
(17) All persons have the right not to be enslaved. Forced labor shall not exist within Germany other than as punishment for a crime for which he shall have been duly convicted in accordance with law.
(18) The people shall be free from all searches and seizures except by a specific warrant in accordance with law, which shall name the time, manner, place, and things sought or searched.
(19) The right to property shall include the right to acquire, use, and dispense with that property. Property shall not be seized without just and speedy compensation.
(20) Men and women may be required to serve in the armed forces, federal border police, or in a civil defense organization upon reaching the age of eighteen.
(21) No German may be deprived of his citizenship except by applicable law, unless it shall result in the person becoming stateless as a result.
(22) No German shall be extradited to a foreign country except by treaty between Germany and the foreign country explicitly stating the conditions thereof.
(23) Persons of German ancestry shall have the right of return to Germany in accordance to law.
(24) Persons persecuted on political or religious grounds shall have the right of asylum in accordance with law.
(25) The freedom of speech, press, education, teaching, assembly, correspondence, association, privacy of correspondence, property, or asylum shall not include the right to overthrow the constitution or the republican form of government, and such person or persons shall forfeit their basic rights in accordance to law.
(26) The preceding basic rights shall bind the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary as directly applicable law.
The German President would have a six year term, with one reelection, as head of state. The Chancellor would be head of government. The Bundestag would consist of the upper house (Landtag) and lower house (Volkstag). From the end of WW2 until 1991, Germany would remain divided between east and west. Germans living in all other countries of Europe were expelled to Germany. The Gottschee Germans were deported to Austria, as were all other German-speakers, including Transylvanian Saxons, from the former Austria-Hungary, to Austria. The Volga Germans were resettled in the now East Germany, adding around 950,000 new persons, along with another roughly 2.8 million from Soviet Europe to be moved into East Germany.
The Germany that came out of the war had 14 states (Bremen, Hamburg, Lübeck, West Berlin, Bavaria, Baden, Württemberg, Alsace-Lorraine, Rhineland, Palatinate, Hessen, Lower Saxony, Oldenburg, Schleswig-Holstein), while the Soviet sector, which became East Germany, had 11 states (Mecklenburg, Pomerania, Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Saxony, Upper Silesia, Lower Silesia, West Prussia, East Prussia, Berlin) which would be converted into 22 Bezirke (districts) so as to more effectively manage them and remove historic ties to the former states. The Berliner Schloss is left in ruin during the entire reign of East Germany. East Germany paid reparations to Poland and the USSR in the form of agricultural output and industrial output. West Germany paid monetary compensation to the west, but when the US put bases in West Germany, the cost of those bases was deducted from the reparations to the US.
West Germany becomes a capitalist beacon, but not in the model of the United States, but rather a European model. Markets are little regulated beyond customer safety, measurements and such. Health care is privatized with insurance for emergencies, while elderly have drug, doctor, and routine procedure insurance plans similar to US medicare, but with more private innovation to reduce the federal outlays. Social insurance does exist, but is funded by private contributions like the US 401k, along with taxes up to 5% to ensure everyone gets something, and people can contribute up to 30% of their income to their social insurance (for retirement, unemployment, and disability). Federal income tax cannot exceed 15%, and state income tax cannot exceed 10%. The West German Mark is introduced in 1948 and West Germany undergoes its Wirtschaftwunder much as in OTL. The West German government, due to Confederate insistence, is much leaner than it had been under the German Empire, Weimar Republic, or Nazi Germany, and is about midway between that of the CS and US, with its regulation and taxation closer to that of the CSA.
East Germany is more capable than OTL since it has Silesian industry, though it was hindered due to Soviet attempts to dismantle and transport back to the USSR initially. Once that stopped, East Germany became the industrial giant of the Warsaw Pact, though its one-party rule, over-regulation, monetary controls, and oppressive spy grid made economic innovation grind to a halt. By the 1980s there were serious signs of trouble, and by 1989, even the excess industrial capacity of Silesia was grinding to a halt as communism faltered.
Once communism fell and the two Germanies reunited, however, West Germany created a plan to bring the east up to western standards, whereby eastern companies would be invested in by the west, given loans with favorable terms, and use those loans to purchase modern equipment to replace old, worn out, and outdated equipment. Eastern German companies struggled through the 1990s but with West German aid, they were able to make the turnaround after a few years.

Continental United States (1948)
After its war with the Confederates, the United States signed a treaty which recognized their new border at the 37th parallel west of the Mississippi, aside from the 'Nevada Notch,' and the Confederates would recognize West Virginia and Missouri as US territory, and both would resume peaceful relations afterwards. The US went on to acquire the Solomon Islands, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, the Marshall Islands, and St Barts. During the war, the US occupied Greenland, a Danish territory, and would buy it in 1948 once the Soviets made their moves in Germany that same year to create a satellite nation. This United States is much like our United States, with a federal reserve, income tax, and much the same history, save the loss of the southern portion in 1865. Its presidents were largely the same, and included Woodrow Wilson, whose parents chose to remain in the US by moving to Maryland. This United States also imported Nazi scientists via Operation Paperclip, but shared the scientific knowledge with the Confederate States, which participated in the operation but would not accept any Nazis into their country, as the distaste for the ideology wouldn't allow it.

Continental Confederate States
The Confederate States were a devastated nation that barely survived their war of secession. Sherman and Grant destroyed as much private property as they could, and kept up the heat as much as they could to use the manpower advantage. But the Confederates turned the tide at Atlanta with Johnston against Sherman, and the Cleburne Memorial's being put into effect in 1864 solved the manpower problems. Aside from its new 37th parallel border, the Confederates stumbled into a near-war with Mexico that they negotiated out of with France, and purchased Alaska from the Russians in exchange for not prosecuting John Turchin and promising a good deal on cotton exports. This version of the CSA purchased the Dominican Republic for its resources (land for tobacco, sugar, cocoa, coffee), and found itself stumbling into war with Spain over Cuba due to its officers helping Cuban rebels; this resulted in the acquisition, after an 11-month war, of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Mariana Islands. Spain sold the Philippines to the US to help pay for the war costs afterwards. Rebuilding was in the Confederate interest, as the British and French interest and helped the economy rebound quickly. This CSA progressed forward to such a point that by 1896, blacks had the constitutional right to vote, though it would be until 1921 when effective legislation would pass that ensured it. Hawaii was annexed in 1874 after attempted coups by the US and UK, seeking protection with the CS. The CS joined WW1 with the destruction of the Lusitania, the US following a few months afterwards. The CS joined WW2 when its fleet at Pearl Harbor was attacked. This CSA has a much lower government footprint than the United States, such that, even after the second world war, Confederates had little to no interactions with their national government, the states being more of the focus of their loyalties and interactions. There is no national bank, no national income tax, and only some states have an income tax. Education is a state issue, funded by tuition, not property tax. Income is on par with the United States, about $1350, but without a national income tax, Confederates keep more of their money. Corporations, however, do have an income tax, but it's a flat tax for the duration of the war. War brides were a thing for the Confederates, much more than the US, with French, British, Dutch, Belgian, German, Italian, Australian, New Zealander, and Japanese brides making up over 550,000 new immigrants into the CS, not including children.
-----
1991
Communism collapsed across eastern Europe for a variety of reasons, and in Berlin, the wall came down to the delight of the German people long separated by concrete, barbed wire, and watch towers. Reunification day was October 3, and the eastern territories were reconstituted legally into their original, pre-1914 borders, undoing quite a few border changes made by the former East Germany. Underground churches, funded by a number of Confederates secretly, kept religion alive in the east, and hope in a brighter future. After the fall of the wall, eastern Germans did flood west, but investment and people flowed east as well. Per the treaty at the end of WW2, the US, CS, UK, and Russia must agree to German reunification.
2000
------
European unification proceeds with the Euro. Economic Union grows as the Schengen border agreement takes place, and Straßburg becomes the seat of the European Parliament, being based in the neutral country of Alsace-Lorraine, a bilingual nation and a symbol for reconciliation and cooperation between France and Germany after the war. The Euro zone begins operation with France, Germany, Spain, Portugal, Austria, Greece, Denmark, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium, Czechia, Slovenia, and Alsace-Lorraine.
2021
-------
After thirty years of unification, the east does continue to have a lower income and level of religion than the west, but both are improving and are continuing to increase. Former buildings, like the Dresden Frauenkirche, the Memorial Church on the side of the Berlin Cathedral, Schloß Charlottenberg, Berliner Schloß, Reich Chancellery (now the Konföderierungskanzlerei), and more are rebuilt to their former appearance and function. The Berliner Schloß is the President of Germany's residence in the city (as of 2009), as Schloß Bellevue did not have room for the President and the government functions for which he is responsible.




