Post by lordroel on Jan 20, 2017 13:22:28 GMT
What if: Operation Sealion, summary of an exercise held in 1974.


In 1974 a major wargame conducted at Royal Military Academy Sandhurst in 1974 was held. Its aim was find out what might have happened had Nazi Germany launched Operation Sea Lion, their planned invasion of southeast England during World War II, in September 1940. The wargame was organized by the Daily Telegraph and Dr Paddy Griffith from the Department of War Studies at Sandhurst. The British umpires were Air Chief Marshal Christopher Foxley-Norris, Rear Admiral Teddy Gueritz and Major General Glyn Gilbert. The German umpires were General Adolf Galland (air), Admiral Friedrich Ruge (naval) and General Heinrich Trettner (land). After the game's conclusion, the umpires unanimously concluded that the invasion was a devastating defeat for the German invasion force.


Scenario
The game was played using a scale model of southeast England, the English Channel, and northern France. Available troops and resources were based on known plans from both sides, and weather conditions were based on contemporary British Admiralty records that had, until then, never been published.
Assumptions
- The German military had taken until September to assemble the shipping necessary for a Channel crossing
- The Luftwaffe had not established air supremacy.
- The Luftwaffe had continued to bomb London.
- The Germans had only converted river barges available as transport ships.
- The invasion fleet was largely unmolested in the crossing.
Orbats of the British and German forces
Hitler's Directive No.16
Hitler's Directive No.17
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels at Embarkation Ports
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels converted and collected in the designated assembly areas for Operation Sealion
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels available for Operation Sealion
Kriegsmarine – Intelligence Report on the Royal Navy
Kriegsmarine – Fleet List
Royal Navy – Intelligence Report on German Navy
Royal Navy – Fleet List
Invasion timeline (September 22nd 1940 to September 28th 1940)
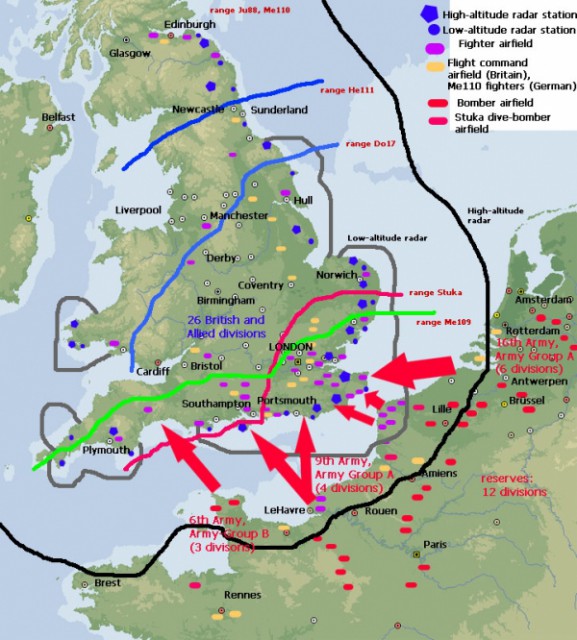
22nd September – morning
The first wave of a planned 330,000 men hit the beaches at dawn. Elements of 9 divisions landed between Folkestone and Rottingdean (near Brighton). In addition 7th FJ Div landed at Lympne to take the airfield.
The invasion fleet suffered minor losses from MTBs during the night crossing, but the RN had already lost one CA and three DDs sunk, with one CA and two DDs damaged, whilst sinking three German DDs. Within hours of the landings which overwhelmed the beach defenders, reserve formations were despatched to Kent. Although there were 25 divisions in the UK, only 17 were fully equipped, and only three were based in Kent, however the defence plan relied on the use of mobile reserves and armoured and mechanised brigades were committed as soon as the main landings were identified.
Meanwhile the air battle raged, the Luftwaffe flew 1200 fighter and 800 bomber sorties before 1200 hrs. The RAF even threw in training planes hastily armed with bombs, but the Luftwaffe were already having problems with their short ranged Me 109s despite cramming as many as possible into the Pas de Calais.
22nd – 23rd September
The Germans had still not captured a major port, although they started driving for Folkestone. Shipping unloading on the beaches suffered heavy losses from RAF bombing raids and then further losses at their ports in France.
The U-Boats, Luftwaffe and few surface ships had lost contact with the RN, but then a cruiser squadron withsupporting DDs entered the Channel narrows and had to run the gauntlet of long range coastal guns, E-Boats and 50 Stukas. Two CAs were sunk and one damaged. However a diversionary German naval sortie from Norway was completely destroyed and other sorties by MTBS and DDs inflicted losses on the shipping milling about in the Channel. German shipping losses on the first day amounted to over 25% of their invasion fleet, especially the barges, which proved desperately unseaworthy.
23rd Sept dawn – 1400 hrs.
The RAF had lost 237 planes out 1048 (167 fighters and 70 bombers), and the navy had suffered enough losses such that it was keeping its BBs and CVs back, but large forces of DDs and CAs were massing. Air recon showed a German buildup in Cherbourg and forces were diverted to the South West.
The German Navy were despondant about their losses, especially as the loss of barges was seriously dislocating domestic industry. The Army and Airforce commanders were jubilant however, and preperations for the transfer of the next echelon continued along with the air transport of 22nd Div, despite Luftwaffe losses of 165 fighters and 168 bombers. Out of only 732 fighters and 724 bombers these were heavy losses. Both sides overestimated losses inflicted by 50%.
The 22nd Div airlanded successfully at Lympne, although long range artillery fire directed by a stay-behind commando group interdicted the runways. The first British counterattacks by 42nd Div supported by an armoured brigade halted the German 34th Div in its drive on Hastings. 7th Panzer Div was having difficulty with extensive anti-tank obstacles and assault teams armed with sticky bombs etc. Meanwhile an Australian Div had retaken Newhaven (the only German port), however the New Zealand Div arrived at Folkestone only to be attacked in the rear by 22nd Airlanding Div. The division fell back on Dover having lost 35% casualties.
Sep 23rd 1400 – 1900 hrs
Throughout the day the Luftwaffe put up a maximum effort, with 1500 fighter and 460 bomber sorties, but the RAF persisted in attacks on shipping and airfields. Much of this effort was directed for ground support and air resupply, despite Adm Raeders request for more aircover over the Channel. The Home Fleet had pulled out of air range however, leaving the fight in the hands of 57 DDs and 17 CAs plus MTBs. The Germans could put very little surface strength against this. Waves of DDs and CAs entered the Channel, and although two were sunk by U-Boats, they sank one U-Boat in return and did not stop. The German flotilla at Le Havre put to sea (3 DD, 14 E-Boats) and at dusk intercepted the British, but were wiped out, losing all their DDs and 7 E-Boats.
The Germans now had 10 divisions ashore, but in many cases these were incomplete and waiting for their second echelon to arrive that night. The weather was unsuitable for the barges however, and the decision to sail was referred up the chain of command.
23rd Sep 1900 – Sep 24th dawn
The Fuhrer Conference held at 1800 broke out into bitter inter-service rivalry – the Army wanted their second echelon sent, and the navy protesting that the weather was unsuitable, and the latest naval defeat rendered the Channel indefensible without air support. Goring countered this by saying it could only be done by stopped the terror bombing of London, which in turn Hitler vetoed. The fleet was ordered to stand by.
The RAF meanwhile had lost 97 more fighters leaving only 440. The airfields of 11 Group were cratered ruins, and once more the threat of collapse, which had receded in early September, was looming. The Luftwaffe had lost another 71 fighters and 142 bombers. Again both sides overestimated losses inflicted, even after allowing for inflated figures.
On the ground the Germans made good progress towards Dover and towards Canterbury, however they suffered reverses around Newhaven when the 45th Div and Australians attacked. At 2150 Hitler decided to launch the second wave, but only the short crossing from Calais and Dunkirk. By the time the order reached the ports, the second wave could not possibly arrive before dawn. The 6th and 8th divisions at Newhaven, supplied from Le Havre, would not be reinforced at all.
Sep 24th dawn – Sep 28th
The German fleet set sail, the weather calmed, and U-Boats, E-Boats and fighters covered them. However at daylight 5th destroyer flotilla found the barges still 10 miles off the coast and tore them to shreds. The Luftwaffe in turn committed all its remaining bombers, and the RAF responded with 19 squadrons of fighters. The Germans disabled two CAs and four DDs, but 65% of the barges were sunk. The faster steamers broke away and headed for Folkestone, but the port had been so badly damaged that they could only unload two at a time.
The failure on the crossing meant that the German situation became desperate. The divisions had sufficient ammunition for 2 to 7 days more fighting, but without extra men and equipment could not extend the bridgehead. Hitler ordered the deployment on reserve units to Poland and the Germans began preparations for an evacuation as further British attacks hemmed them in tighter. Fast steamers and car ferries were assembled for evacuation via Rye and Folkestone.
Of 90,000 troops who landed on 22nd September, only 15,400 returned to France, the rest were killed or captured.
Original text: Operation Sealion - summary of an exercise held at the Staff College, Sandhurst in 1974.


In 1974 a major wargame conducted at Royal Military Academy Sandhurst in 1974 was held. Its aim was find out what might have happened had Nazi Germany launched Operation Sea Lion, their planned invasion of southeast England during World War II, in September 1940. The wargame was organized by the Daily Telegraph and Dr Paddy Griffith from the Department of War Studies at Sandhurst. The British umpires were Air Chief Marshal Christopher Foxley-Norris, Rear Admiral Teddy Gueritz and Major General Glyn Gilbert. The German umpires were General Adolf Galland (air), Admiral Friedrich Ruge (naval) and General Heinrich Trettner (land). After the game's conclusion, the umpires unanimously concluded that the invasion was a devastating defeat for the German invasion force.


Scenario
The game was played using a scale model of southeast England, the English Channel, and northern France. Available troops and resources were based on known plans from both sides, and weather conditions were based on contemporary British Admiralty records that had, until then, never been published.
Assumptions
- The German military had taken until September to assemble the shipping necessary for a Channel crossing
- The Luftwaffe had not established air supremacy.
- The Luftwaffe had continued to bomb London.
- The Germans had only converted river barges available as transport ships.
- The invasion fleet was largely unmolested in the crossing.
Orbats of the British and German forces
Hitler's Directive No.16
Hitler's Directive No.17
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels at Embarkation Ports
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels converted and collected in the designated assembly areas for Operation Sealion
Kriegsmarine – List of Vessels available for Operation Sealion
Kriegsmarine – Intelligence Report on the Royal Navy
Kriegsmarine – Fleet List
Royal Navy – Intelligence Report on German Navy
Royal Navy – Fleet List
Invasion timeline (September 22nd 1940 to September 28th 1940)

22nd September – morning
The first wave of a planned 330,000 men hit the beaches at dawn. Elements of 9 divisions landed between Folkestone and Rottingdean (near Brighton). In addition 7th FJ Div landed at Lympne to take the airfield.
The invasion fleet suffered minor losses from MTBs during the night crossing, but the RN had already lost one CA and three DDs sunk, with one CA and two DDs damaged, whilst sinking three German DDs. Within hours of the landings which overwhelmed the beach defenders, reserve formations were despatched to Kent. Although there were 25 divisions in the UK, only 17 were fully equipped, and only three were based in Kent, however the defence plan relied on the use of mobile reserves and armoured and mechanised brigades were committed as soon as the main landings were identified.
Meanwhile the air battle raged, the Luftwaffe flew 1200 fighter and 800 bomber sorties before 1200 hrs. The RAF even threw in training planes hastily armed with bombs, but the Luftwaffe were already having problems with their short ranged Me 109s despite cramming as many as possible into the Pas de Calais.
22nd – 23rd September
The Germans had still not captured a major port, although they started driving for Folkestone. Shipping unloading on the beaches suffered heavy losses from RAF bombing raids and then further losses at their ports in France.
The U-Boats, Luftwaffe and few surface ships had lost contact with the RN, but then a cruiser squadron withsupporting DDs entered the Channel narrows and had to run the gauntlet of long range coastal guns, E-Boats and 50 Stukas. Two CAs were sunk and one damaged. However a diversionary German naval sortie from Norway was completely destroyed and other sorties by MTBS and DDs inflicted losses on the shipping milling about in the Channel. German shipping losses on the first day amounted to over 25% of their invasion fleet, especially the barges, which proved desperately unseaworthy.
23rd Sept dawn – 1400 hrs.
The RAF had lost 237 planes out 1048 (167 fighters and 70 bombers), and the navy had suffered enough losses such that it was keeping its BBs and CVs back, but large forces of DDs and CAs were massing. Air recon showed a German buildup in Cherbourg and forces were diverted to the South West.
The German Navy were despondant about their losses, especially as the loss of barges was seriously dislocating domestic industry. The Army and Airforce commanders were jubilant however, and preperations for the transfer of the next echelon continued along with the air transport of 22nd Div, despite Luftwaffe losses of 165 fighters and 168 bombers. Out of only 732 fighters and 724 bombers these were heavy losses. Both sides overestimated losses inflicted by 50%.
The 22nd Div airlanded successfully at Lympne, although long range artillery fire directed by a stay-behind commando group interdicted the runways. The first British counterattacks by 42nd Div supported by an armoured brigade halted the German 34th Div in its drive on Hastings. 7th Panzer Div was having difficulty with extensive anti-tank obstacles and assault teams armed with sticky bombs etc. Meanwhile an Australian Div had retaken Newhaven (the only German port), however the New Zealand Div arrived at Folkestone only to be attacked in the rear by 22nd Airlanding Div. The division fell back on Dover having lost 35% casualties.
Sep 23rd 1400 – 1900 hrs
Throughout the day the Luftwaffe put up a maximum effort, with 1500 fighter and 460 bomber sorties, but the RAF persisted in attacks on shipping and airfields. Much of this effort was directed for ground support and air resupply, despite Adm Raeders request for more aircover over the Channel. The Home Fleet had pulled out of air range however, leaving the fight in the hands of 57 DDs and 17 CAs plus MTBs. The Germans could put very little surface strength against this. Waves of DDs and CAs entered the Channel, and although two were sunk by U-Boats, they sank one U-Boat in return and did not stop. The German flotilla at Le Havre put to sea (3 DD, 14 E-Boats) and at dusk intercepted the British, but were wiped out, losing all their DDs and 7 E-Boats.
The Germans now had 10 divisions ashore, but in many cases these were incomplete and waiting for their second echelon to arrive that night. The weather was unsuitable for the barges however, and the decision to sail was referred up the chain of command.
23rd Sep 1900 – Sep 24th dawn
The Fuhrer Conference held at 1800 broke out into bitter inter-service rivalry – the Army wanted their second echelon sent, and the navy protesting that the weather was unsuitable, and the latest naval defeat rendered the Channel indefensible without air support. Goring countered this by saying it could only be done by stopped the terror bombing of London, which in turn Hitler vetoed. The fleet was ordered to stand by.
The RAF meanwhile had lost 97 more fighters leaving only 440. The airfields of 11 Group were cratered ruins, and once more the threat of collapse, which had receded in early September, was looming. The Luftwaffe had lost another 71 fighters and 142 bombers. Again both sides overestimated losses inflicted, even after allowing for inflated figures.
On the ground the Germans made good progress towards Dover and towards Canterbury, however they suffered reverses around Newhaven when the 45th Div and Australians attacked. At 2150 Hitler decided to launch the second wave, but only the short crossing from Calais and Dunkirk. By the time the order reached the ports, the second wave could not possibly arrive before dawn. The 6th and 8th divisions at Newhaven, supplied from Le Havre, would not be reinforced at all.
Sep 24th dawn – Sep 28th
The German fleet set sail, the weather calmed, and U-Boats, E-Boats and fighters covered them. However at daylight 5th destroyer flotilla found the barges still 10 miles off the coast and tore them to shreds. The Luftwaffe in turn committed all its remaining bombers, and the RAF responded with 19 squadrons of fighters. The Germans disabled two CAs and four DDs, but 65% of the barges were sunk. The faster steamers broke away and headed for Folkestone, but the port had been so badly damaged that they could only unload two at a time.
The failure on the crossing meant that the German situation became desperate. The divisions had sufficient ammunition for 2 to 7 days more fighting, but without extra men and equipment could not extend the bridgehead. Hitler ordered the deployment on reserve units to Poland and the Germans began preparations for an evacuation as further British attacks hemmed them in tighter. Fast steamers and car ferries were assembled for evacuation via Rye and Folkestone.
Of 90,000 troops who landed on 22nd September, only 15,400 returned to France, the rest were killed or captured.
Original text: Operation Sealion - summary of an exercise held at the Staff College, Sandhurst in 1974.




